Introduction
Wood flooring combines natural elegance with advanced engineering to create a durable and timeless surface. But what if the secret behind its durability and beauty lies in material science? In this article, we’ll explore how material science enhances wood flooring, from understanding its grain structure to integrating synthetic materials that improve strength and performance. Whether you’re curious about the science behind wood or looking for insights on material science engineering, we’ll guide you through the key innovations shaping the future of wood flooring. Let’s dive into how material science is transforming wood into a more sustainable and long-lasting flooring solution.
Material Science Fundamentals for Wood Flooring
What is Material Science?
Material science is a multidisciplinary field focusing on understanding and manipulating the properties of matter.It answers questions such as ‘What is material science?’ and ‘What is a material in science? Material scientists study the composition, structure, and behavior of materials—from metals and ceramics to polymers and wood. In the wood flooring sector, material science informs us about wood’s natural properties, including its strength, grain, and microstructure.
Key Points:
- Definition: Material science explores the relationship between the structure of materials at the atomic or molecular scale and their macroscopic properties.
- Applications: In wood flooring, these principles are used to optimize properties such as durability, resistance to wear, and aesthetic value.
- Educational Path: For those interested in the field, understanding what is materials science engineering and what is a material science degree is important, as courses and research in these areas drive advancements in wood flooring and other industries.
How to Learn Material Science
For enthusiasts and professionals alike, there are multiple pathways to learn more about material science. Whether through formal education—such as pursuing a degree in material science engineering—or self-study using online resources, there are many ways to build a strong foundational knowledge. Consider these steps to start your journey:
- Enroll in Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses in materials science.
- Engage in Hands-On Projects: Experiment with wood samples to observe properties like what is hardness in material science in a real-world setting.
For further guidance, refer to MIT OpenCourseWare for free resources and research material from a leading authority in the field.
Wood Flooring Material Properties
Understanding the properties of wood and engineered wood products is crucial for producing high-quality flooring. Material science explores these properties using both theoretical analysis and practical experiments.
Wood Structure and Grain Characteristics
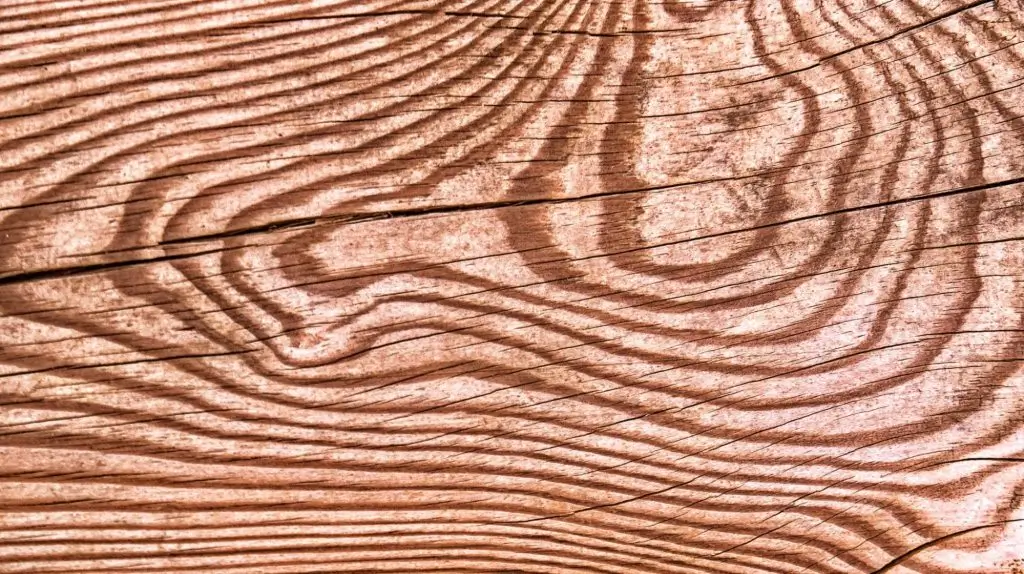

The beauty and performance of wood flooring are significantly influenced by its grain. Researchers and manufacturers often ask, what is grain in material science and what is grain size in material science, as these factors affect both the appearance and structural integrity of the final product.
Grain and Aesthetics
The grain of wood is an essential characteristic that influences both the performance and aesthetic appeal of wood flooring. It refers to the orientation, texture, and appearance of wood fibers, which can vary significantly between different wood species, and even within a single board. Understanding the key aspects of wood grain helps to determine how the material behaves and enhances its application in flooring. The primary factors to consider include:
Key Aspects of Wood Grain:
- Grain Orientation: This refers to the direction in which the wood fibers are aligned. It affects the wood’s ability to expand and contract with changes in moisture levels and how it responds to applied loads.
- Grain Density: The density of the wood grain impacts its strength and overall durability. Denser grain typically results in a harder, more robust material that is more resistant to wear and tear.
- Visual Texture: The grain’s texture has a significant influence on the floor’s aesthetic appeal. Whether it’s fine, straight, or wavy, the pattern creates visual interest and can complement various interior design styles.
By considering these aspects of wood grain, industry professionals can select the right materials that balance durability and aesthetics, leading to a superior finished product.
For more insights, refer to internal resources on wood grain analysis and external research articles on wood science.
Mechanical Properties and Performance

The mechanical performance of wood flooring is critical in determining its durability and suitability for various environments. Key parameters such as hardness, strength, and stress all play a vital role in assessing how well the material withstands daily wear and tear. These properties are fundamental in material science, influencing the flooring’s ability to resist damage and maintain its appearance over time.
Hardness and Durability
- Hardness: Defines the ability of wood to resist indentation and abrasion.
- Tests: Hardness can be assessed using standardized tests such as the Janka hardness test.
Table: Janka Hardness Values for Common Wood Species
| Wood Species | Janka Hardness (lbf) | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Red Oak | 1290 | Traditional hardwood flooring |
| Maple | 1450 | High-traffic areas |
| Walnut | 1010 | Decorative flooring |
| Bamboo (Engineered) | 1380 | Sustainable flooring options |
Using tables like the one above enhances readability and provides clear comparisons.
Strength and Stress Analysis
- Strength: Refers to the ability of wood to withstand loads without failure.
- Stress: The internal forces that develop in response to external loads.
Engineers use simulation models and field testing to measure these properties accurately, ensuring that wood flooring maintains its integrity under various conditions.
Microstructure and Phase Analysis
Understanding what is microstructure in material science and what is phase in material science is essential to improving the performance and stability of wood flooring. The microstructure of wood, including its cellular composition and fiber alignment, directly affects how the material behaves under varying environmental conditions such as humidity, heat, and mechanical stress.
Why Microstructure Matters
The internal structure of wood influences key performance indicators:
- Moisture response: Tightly packed fibers may reduce swelling or warping.
- Thermal behavior: Micro-level porosity affects heat retention and expansion.
- Mechanical strength: Fiber orientation enhances resistance to impact and wear.
Phase Transformations and Surface Treatments
Although “phase” in material science traditionally refers to transitions between solid, liquid, and gas states, in the context of wood flooring, it often relates to chemical and structural changes during treatments:
- Adhesive curing: As bonding agents transition from liquid to solid, their phase behavior affects bonding strength.
- Coating hardening: Surface finishes undergo phase changes during drying, influencing durability and appearance.
Heat Treatment and Quenching Techniques
In metal engineering, what is quenching in material science refers to rapid cooling to enhance hardness. A comparable method is applied in wood flooring heat treatments, where temperature is carefully controlled to:
- Reduce internal stress.
- Improve dimensional stability.
- Enhance surface hardness without compromising the material’s integrity.
Advanced Materials Used in Wood Flooring
In addition to natural wood, modern wood flooring often incorporates advanced materials. These include both composite structures and innovative synthetic materials that enhance performance and stability.
Composite and Synthetic Materials
Wood flooring today is not limited to traditional natural wood. Many products are engineered with composites and synthetic materials. These can offer improved durability, lower cost, or enhanced environmental performance.
What are Composites in Material Science?
Composites refer to materials made from two or more constituent materials with differing properties. In the wood flooring industry, composites might include:
- Engineered Wood Products: Such as plywood, high-density fiberboard (HDF), and laminated flooring.
- Reinforced Composites: Integrating natural fibers with resins to enhance mechanical properties.
These materials often provide better dimensional stability and moisture resistance compared to solid wood.
Synthetic Materials in Wood Flooring
Modern flooring may incorporate what is a synthetic material in science such as polymers or engineered resins. These materials offer:
- Enhanced Durability: Improved resistance to wear, scratches, and moisture.
- Design Flexibility: Easier fabrication of patterns and surface textures that mimic natural wood.
For readers seeking deeper insights, be sure to check out our in-depth wood flooring comparison guide for practical product evaluations. Additionally, this industry report by the American Wood Council provides authoritative data and trends that can further inform your decisions.
Raw and Natural Materials
The foundation of any high-quality wood flooring lies in its raw and natural materials. Understanding what are raw materials in science and what are natural materials in science helps manufacturers, designers, and consumers make informed choices that enhance both performance and sustainability.
Natural Materials in Wood Flooring
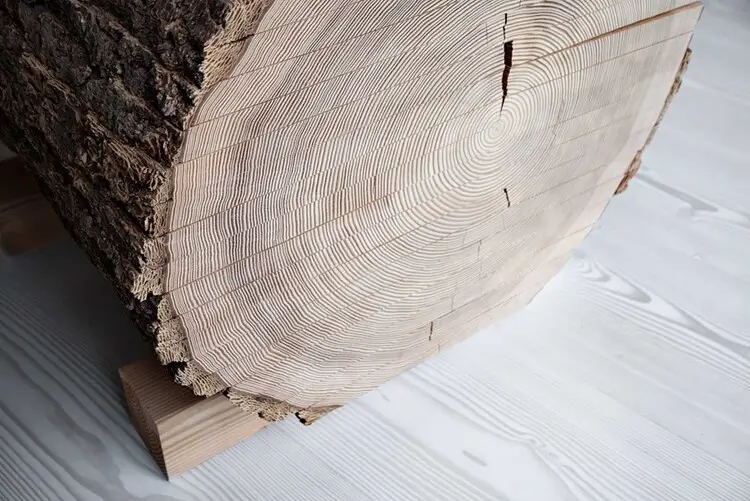

Natural wood remains a preferred material due to its beauty and eco-friendly properties. When exploring what are natural materials in science, consider:
- Species Variation: Different tree species offer unique characteristics, affecting grain pattern, hardness, and color.
- Environmental Impact: Sourcing sustainably harvested wood reduces environmental impact.
Parent Material and Its Influence
What is parent material in science refers to the original material from which wood is derived. This includes not only the wood fibers themselves but also the environmental and geological conditions that affect wood quality. For example:
- Soil Composition and Climate: Influence the growth patterns, density, and resilience of trees.
- Forest Management Practices: Affect the overall quality and sustainability of the harvested wood.
Detailed Analysis and Comparative Overview
To further elucidate the role of material science in wood flooring, let’s summarize key concepts through a comparative overview. This section incorporates diagrams, bullet lists, and charts to facilitate quick understanding.
Comparative Overview Table
| Aspect | Traditional Wood | Engineered Wood/Composite | Synthetic Enhancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain Characteristics | Natural, variable | Engineered for consistency | Mimics natural grain through printing |
| Hardness | Varies by species | Uniform hardness due to layering | Customizable with additives |
| Microstructure | Cellular structure inherent | Optimized for stability | Engineered microstructures for enhanced performance |
| Moisture Resistance | Susceptible to humidity | Improved through adhesives and layers | High resistance using synthetic resins |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, sustainable (if sourced ethically) | Recyclable with careful production | Depends on materials used |
Key Questions Answered
Throughout the article, we have naturally integrated critical keywords and addressed key questions:
1. What is hardness in material science?
Hardness measures resistance to scratches and wear. In wood flooring, higher hardness means better durability.
2. What is strength in material science?
Strength is a material’s ability to resist breaking or deforming. It includes tensile, compressive, and bending strength.
3. What is stress in material science?
Stress refers to internal force under external load. It helps predict wood behavior under pressure or humidity changes.
4. What is grain in material science?
Grain describes the direction and texture of wood fibers, affecting appearance and how wood reacts to moisture.
5. What is grain size in material science?
Grain size refers to the scale of fibers. Smaller grain size often means smoother texture and higher strength.
6. What are raw materials in science?
Raw materials are the basic substances used in production, like wood logs, adhesives, and coatings.
7. What are natural materials in science?
Natural materials come from nature with minimal processing, such as solid hardwood from sustainably managed forests.
8.What is material science?
Material science is the study of the properties, composition, and behavior of matter. In the context of wood flooring, it helps to explain how and why wood behaves under various conditions.
9.What is a material in science?
A material is any substance with defined properties that can be engineered for specific purposes. This definition applies widely, including in the field of wood flooring.
10.What is materials science engineering?
This discipline applies the principles of material science to develop, test, and improve products. In wood flooring, engineers use material science to optimize properties such as strength and durability.
11.What is a material science degree?
A material science degree equips students with deep insights into how materials work, preparing them for careers in engineering and research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, material science plays a crucial role in advancing wood flooring. By understanding key principles like material properties, grain structure, and composite innovations, industry professionals can significantly improve the performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of wood flooring products. As technology continues to evolve, the fusion of traditional methods and modern material science will shape the future of sustainable and high-quality wood flooring. Embrace these advancements to stay ahead in the industry and create superior flooring solutions that stand the test of time.




